Introduction to Nuclear Criticality Safety
REVIEW TOPICS PART IV
Continuing . . .
MEAN FREE PATHS
The average distance that a neutron travels without interacting is known as the mean free path. We can define a probability density ( ≈ distribution) function for first collision in our beam problem:
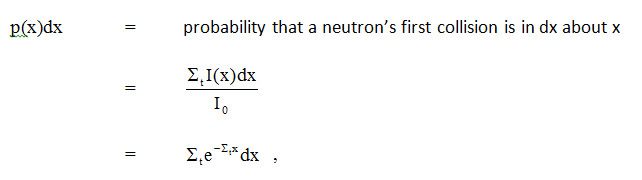
which means the probability density function (pdf) for first collision is p(x) = 
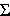 te-
te-
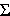 t x. We can use this pdf to obtain averages. For example:
t x. We can use this pdf to obtain averages. For example:
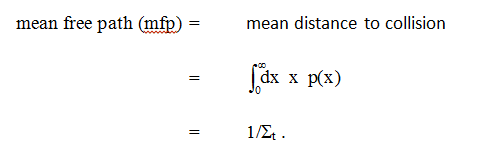
The mean free path is the reciprocal of the macroscopic cross section. It follows from their definitions that macroscopic cross sections are additive in the same way that microscopic cross sections are:
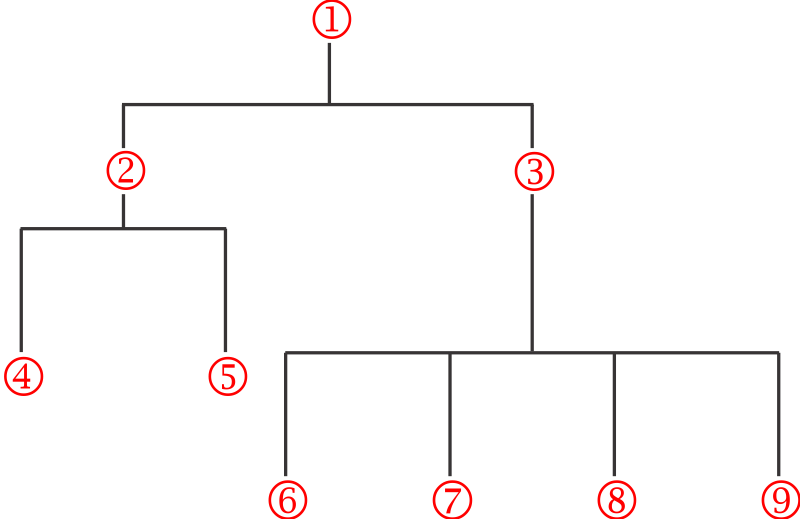
Match the numbers within the hierarchy with the proper terms: Σt Σs Σa Σin Σe Σs Σn,2n Σn,α Σ
In addition, given:
a mixture of nuclides: YA, YB, ....,
with number densities: NA, NB, ....,
and microscopic cross sections: σx A, σx B, .....,
then for any type, x, of interaction, the macroscopic cross section for the mixture is: