NUCLEAR REACTIONS
Nuclear reactions are taking place when two nuclear particles interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or gamma rays. The following notation is frequently used to describe nuclear reactions (Id., equation 2.34):

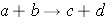
Sometimes a more detailed notation is used since one particle is generally considered to be a projectile while the other particle is taken as a target (Duderstadt & Hamilton 1976, p. 15):
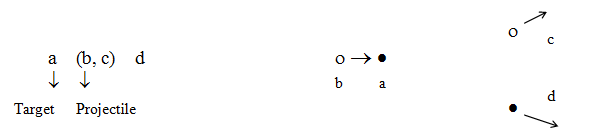
As an example, the reaction

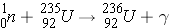
would be written as

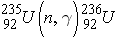
For the reaction a(b,c)d, the reaction energy (or Q-value) is calculated as (Id., equation 2.37):
Q = ((Ma + Mb) - (Mc + Md)) c2
where . . .
M = atomic mass of the nuclide
c = speed of light (converted into energy in a reaction)
Q is expressed in MeV. Recalling that 1 amu is 931.494 MeV, the Q value can be written as
Q = ((Ma + Mb) - (Mc + Md)) 931.494 MeV
Proceed to Part II
After finishing this lesson, complete the form below:

